Recently, Professor Shanshan Xu’s Group from the Institute for Advanced Study of Shenzhen University (IAS) published a research paper titled Mechanism of a long-term controlled drug release system based on simple blended electrospun fibers in an international authoritative journal called Journal of controlled release (Impact Factor 7.901, Chinese Academy of Sciences JCR, TOP).
Drug delivery systems based on electrospun fibers have been under development for many years. There are a number of problems that remain unsolved, such as large-burst drug release, uncontrolled duration of drug release, and incomplete drug release. Previous studies, including some by us, have indicated that drug diffusion and carrier degradation together affect the drug release profile. However, studies of controllable long-term drug release from electrospun membrane systems and the underlying release mechanisms have seldom been reported. Therefore, in this study, electrospun membrane drug delivery systems consisting of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and FDA-approved polymers are fabricated. Different second-component polymers are introduced to change the properties of a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) matrix, thereby altering the drug release behavior. On the basis of observations of morphology, cumulative release profiles, and determinations of release duration, the drug release kinetics and critical characteristics influencing drug release behavior are discussed, clarifying main control factors and mechanisms in each stage.
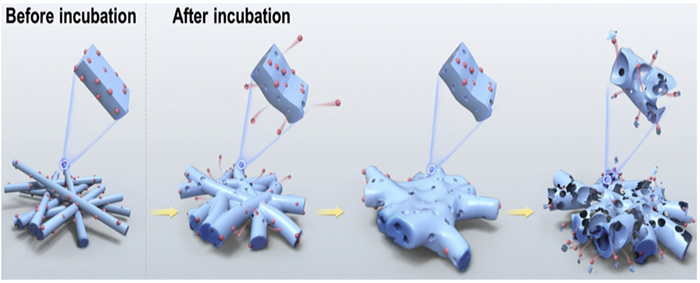
It is found that the drug release profiles can be divided into three stages according to the rate of drug release. Stage I is controlled by fiber swelling and diffusion according to Fick's second rule. Stage II is controlled by diffusion through a fused membrane structure, which results in a very slow drug release. Stage III is controlled by polymer degradation and involves the release of the remaining drug. The results of this study of release mechanisms should provide a basis for adjustments of drug release dosage and duration, thereby contributing to the development of drug delivery systems satisfying clinical requirements.
The corresponding authors are Professor Shanshan Xu from IAS and Ying Liu from The National Center for Nanoscience and Technology. IAS student Jiaen Wu, Dr. Zixin Zhang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and student Jin’ge Gu from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology of China are the first authors. This work was financially supported by the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars, the National Nature Science Foundation of China, Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Project, Shenzhen High-end Talent Project and the National Basic Research Program of China. Shenzhen University is the first completion unit.
The paper is available under the link https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.020.


