Farid Ahmed, Shahzad Iqbal, and Hai Xiong*
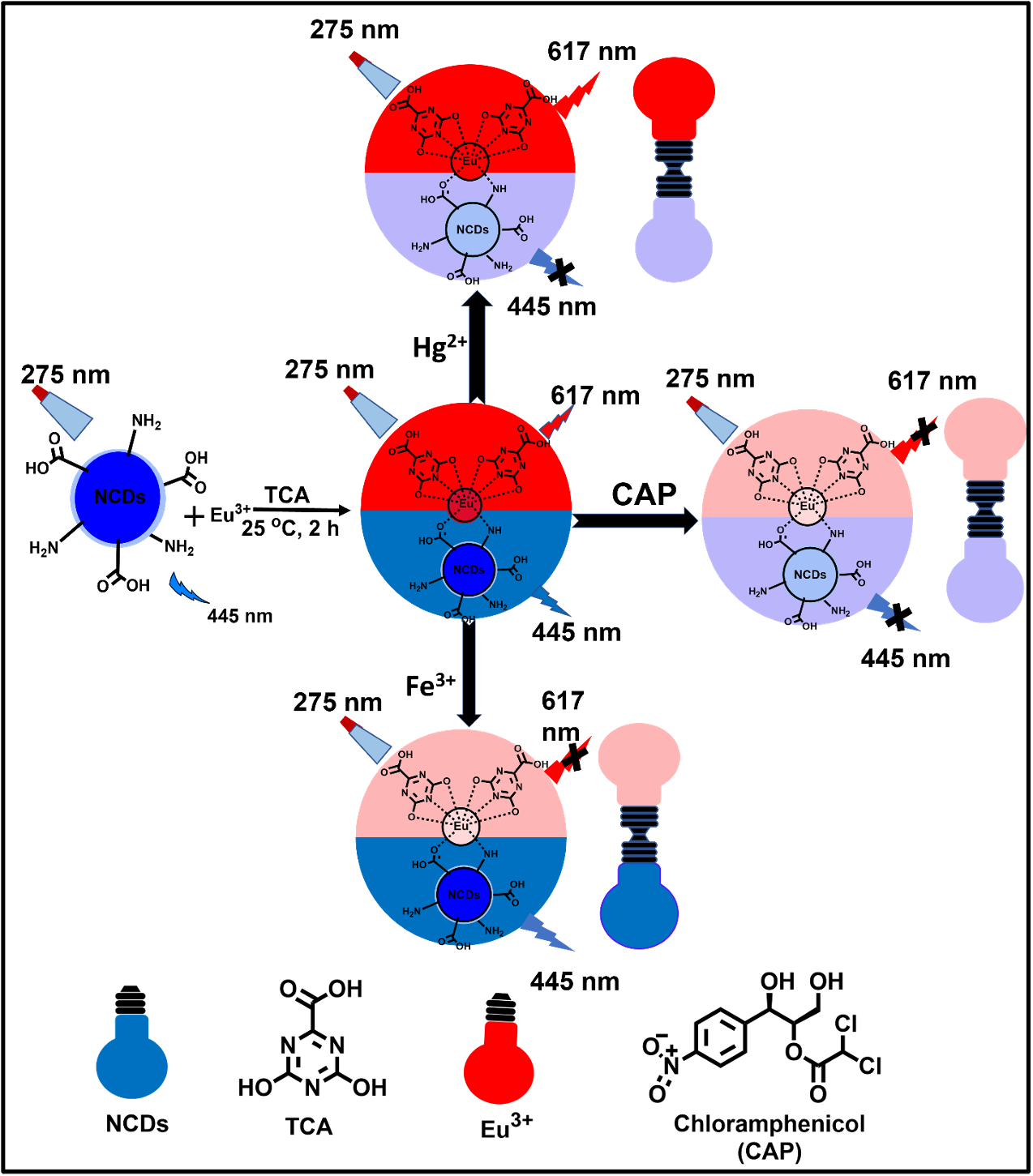
Lanthanide functionalized N-doped carbon dots have potential applications in the development of innovative photoluminescence probes for environmental and biological analytes. In this study, a novel multifunctional dual-emissive fluorescent probe based on europium complex with 4,6’-dihydroxy-1,3,5’-triazine-2-carboxylic acid and N-doped carbon dots (Eu-TCA/NCDs) is reported for the selective detection of chloramphenicol (CAP), Hg2+ and Fe3+ in real samples. At an excitation wavelength (λex = 275 nm), the aqueous solution of the Eu-TCA/NCDs probe exhibited strong fluorescence emission at two different wavelengths (445 and 617 nm). Under the same conditions, the addition of CAP to the probe resulted in significant fluorescence quenching at both emission wavelengths. An excellent linear relationship (R2 = 0.9963) between the concentration of CAP (0.01-50 µM) and fluorescence quenching was observed with a detection limit of 12 nM. Furthermore, the probe demonstrated a ratiometric response in the presence of Hg2+ and Fe3+ ions. The addition of Hg2+ cause substantial quenching at 445 nm while the intensity at 617 nm almost remains unchanged. However, upon addition of Fe3+ the fluorescence intensity at 617 nm decreases sharply while the intensity at 445 nm remains same. Furthermore, the practical applicability of the probe was authenticated by the detection of CAP, Hg2+ and Fe3+ in real samples (with RSD ≤ 2.35%) with a recovery percentage of 95.2-103. These results open a new avenue for developing lanthanide-doped nanocomposites that display white-light-based dual-emissive fluorescence recognition of biological and environmental pollutants.
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen, China (JCYJ20210324095607021 and KQJSCX20180328095517269), and Top Young Talent of the Pearl River Talent Recruitment Program, China.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2022/EN/D2EN00376G?page=search