Recently, the research team led by Dr. Yan Sheng from the Institute of Advanced Study at Shenzhen University published their work on "Modular microfluidics for life sciences" in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology (IF=9.4, TOP in Engineering 1 of Chinese Academy of Sciences). Wu Jialin, a master's student from the Nanophotonics Research Center at Shenzhen University, and Professor Fang Hui are co-first authors of the paper, and Dr. Yan Sheng is the corresponding author. Shenzhen University's Institute of Study Research is the first unit, and the work was also supported by Dr. Zhang Jun from Griffith University in Australia, as well as Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation and Shenzhen Natural Science Fund.
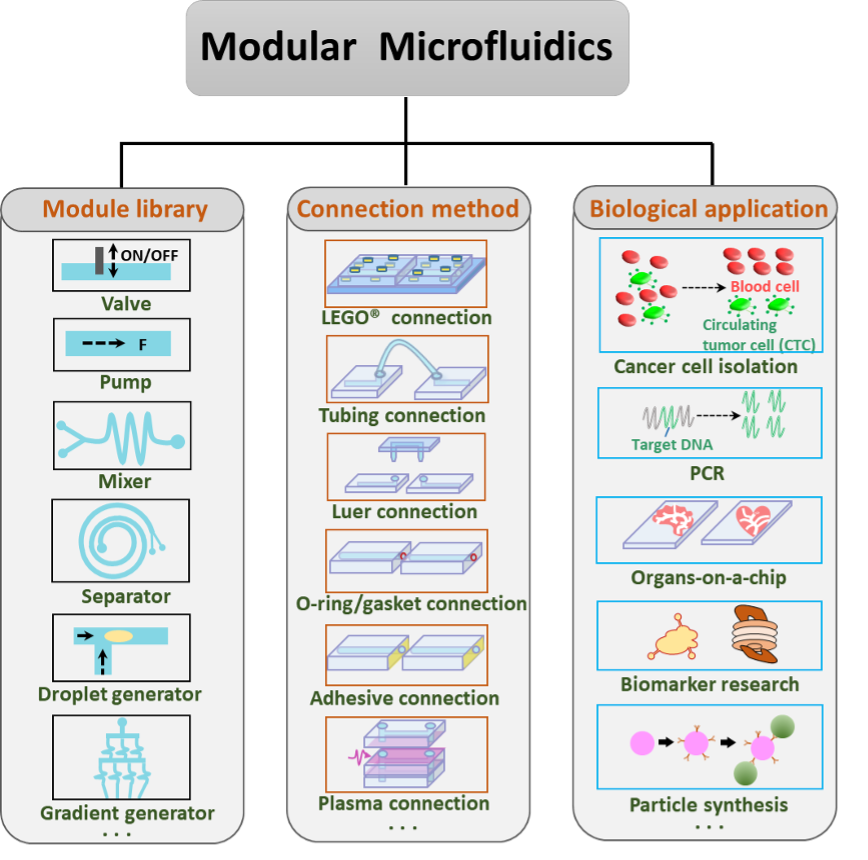
The advancement of microfluidics has enabled numerous discoveries and technologies in life sciences. However, due to the lack of industry standards and configurability, the design and fabrication of microfluidic devices require highly skilled technicians. The diversity of microfluidic devices discourages biologists and chemists from applying this technique in their laboratories. Modular microfluidics, which integrates the standardized microfluidic modules into a whole, complex platform, brings the capability of configurability to conventional microfluidics.
Due to the superior characteristics of modular microfluidics, including portability, on-site deployability, and high customization, Dr. Yan Sheng's research team at the Institute of Advanced Study at Shenzhen University reviewed the latest advances in modular microfluidics research and discussed their future prospects. In this review, the working mechanism of basic microfluidic modules is first introduced, and their feasibility as modular microfluidic components is evaluated. Then, the connection methods between these microfluidic modules are introduced, and the advantages of modular microfluidics in biological applications relative to integrated microfluidics are summarized. Finally, the challenges and future prospects of modular microfluidics are discussed.
Original link: https://jnanobiotechnology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12951-023-01846-x