Professor Meng Li’s group from the Institute of Advanced Study (IAS) of Shenzhen University has published a research paper titled “On-site Screening Method for Bioavailability Assessment of the Organophosphorus Pesticide, Methyl Parathion, and Its Primary Metabolite in Soils by Paper Strip Biosensor” inJournal of Hazardous Materials(impact factor: 14.224; ranked in CAS JCR Q1; TOP). Dr. Zhao Ma, a Post-doc at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) of Shenzhen University is the first author, and Prof. Meng Li is the last corresponding author.
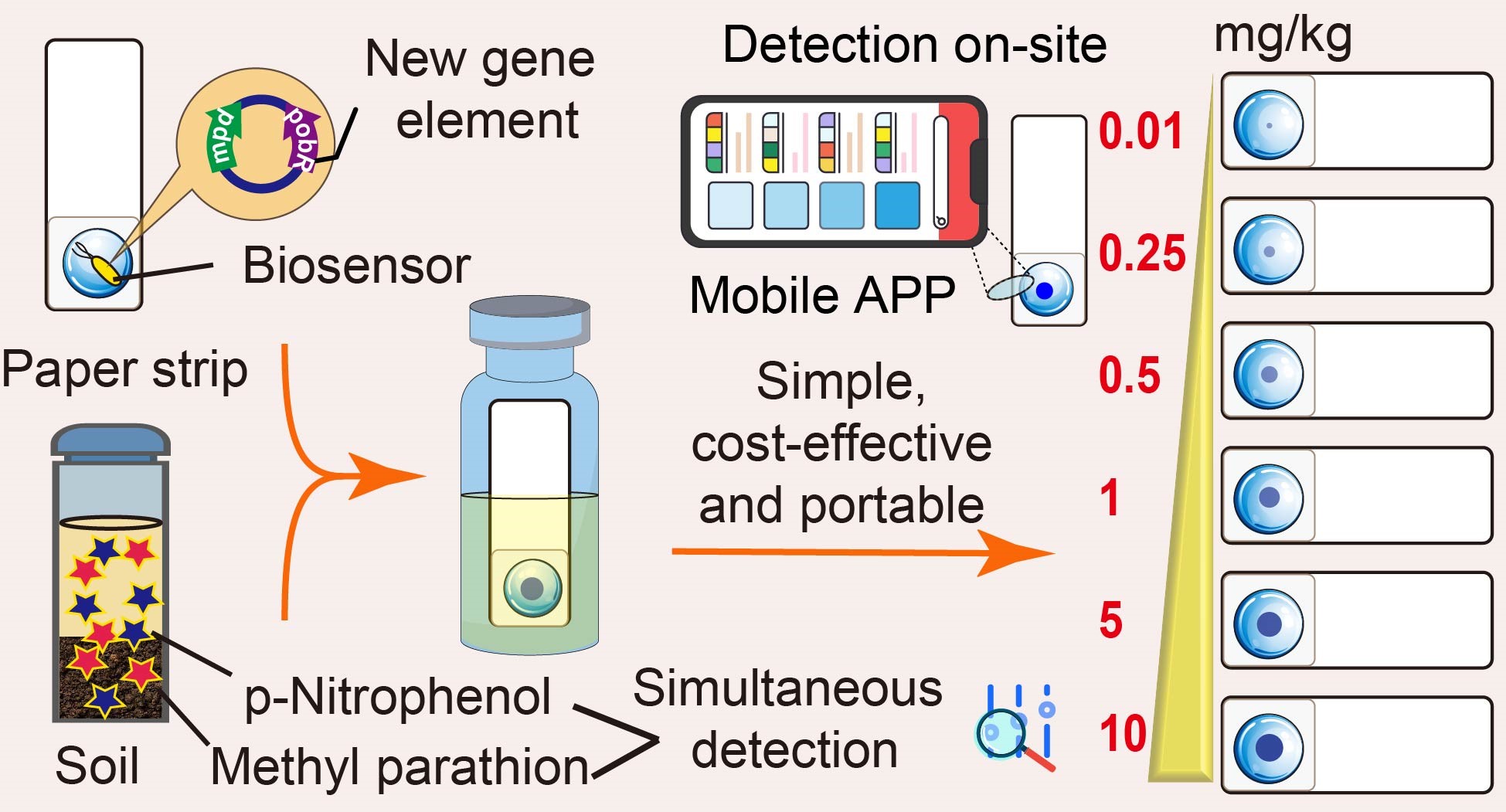
An important public concern worldwide is soil pollution caused by organophosphorus pesticides and their primary metabolites. To protect the public’s health, screening these pollutants on-site and determining their soil bioavailability is important, but doing so is still challenging. This work improved the already-existing organophosphorus pesticide hydrolase (mpd) and transcriptional activator (pobR), and it first designed and constructed a novel biosensor (Escherichia coliBL21/pNP-LacZ) that can precisely detect methyl parathion (MP) and its primary metabolite p-nitrophenol withlow background value. To create a paper strip biosensor,E. coliBL21/pNP-LacZ was fixed to filter paper using bio-gel alginate and sensitizer polymyxin B. According to the calibrations of the paper strip biosensor for soil extracts and standard curve, the color intensity of the paper strip biosensor collected by the mobile app may be used to compute the concentration of MP and p-nitrophenol. This method’s detection limits were 5.41 µg/kg for p-nitrophenol and 9.57 µg/kg for MP. The detection ofp-nitrophenol and MP in laboratory and field soil samples confirmed this procedure. Paper strip biosensoron-site allows for the semi-quantitative measurementof p-nitrophenol and MP levels in soils in a simple, inexpensive, and portable method.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province, and the Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen. The paper is linked athttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131725。