On June 12, 2023, Professors Meng Li and Yang Liu and their teams at the Institute for Advanced Study of Shenzhen University published a research paper titled "Alternative Z-genome biosynthesis pathway shows evolutionary progression from Archaea to phage" in the journal "Nature Microbiology". The study discovered and characterized a variant of the key enzyme PurZ in the Z base synthesis pathway called PurZ0, revealing that PurZ0 is an evolutionary intermediate from the Archaea PurA to the phage PurZ. This finding expands the biological synthesis pathway of the Z base, which is of significant theoretical significance for exploring the origin of Z-genome life. The study is a great achievement of the collaboration between the teams of Professor Yan Zhang from Tianjin University School of Pharmacy, Professor Suwen Zhao from ShanghaiTech University, and Professor Meng Li from Shenzhen University. The first author of the paper is Yang Tong, a Ph.D. student from the School of Pharmacy at Tianjin University, and the co-first authors are Dr. Xinying Wu from ShanghaiTech University and Professor Yang Liu from Shenzhen University.
The balance of nucleotides is strictly regulated to maintain normal cell life and the fidelity of DNA replication. One mechanism is that the nucleotide reductase RNR regulates the balance of the four dNTPs in cells through conformational changes. In addition, the cross-regulation in the de novo purine nucleotide synthesis pathway, where AMP is synthesized from inosine monophosphate (IMP) with GTP as an energy donor, while GMP is synthesized with ATP as an energy donor, is beneficial for purine nucleotides' balance.
Previous study has showed PurZ as a key enzyme, which belongs to the PurA family of adenylosuccinate synthetases. PurA uses GTP as an energy donor and catalyzes the condensation of IMP and aspartic acid, participating in AMP synthesis in the de novo purine synthesis pathway. PurZ, on the other hand, uses ATP as an energy donor and catalyzes the condensation of dGMP and aspartic acid, generating 2-amino-deoxyadenosine phosphate succinate, participating in dZMP synthesis. Other studies suggested that Z base DNA biosynthesis is the third purine synthesis pathway. In fact, dZMP is produced from dGMP and should be an extension of the GMP synthesis pathway. Therefore, the use of ATP by PurZ as an energy donor is an important mechanism for maintaining intracellular purine balance and is an evolutionary necessity. From PurA to PurZ, both substrates have changed, which may have occurred in succession in the evolutionary process, producing an evolutionary intermediate.
This study used sequence similarity network analysis to discover PurZ's variant PurZ0 and proposed that, like PurA, PurZ0 uses GTP as an energy donor based on the similarities and differences between its and PurZ and PurA's substrate binding sites. The study characterized PurZ0 from five different species using in vitro enzyme activity detection methods such as high-resolution mass spectrometry, ultraviolet spectroscopy, and colorimetry. PurZ0 catalyzed the condensation of dGMP and Asp with GTP as an energy donor, generating 2-amino-deoxyadenosine phosphate succinate. The crystal structure of the PurZ0-GTP complex was analyzed and found to be highly similar to that of PurA's GTP binding pocket. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that PurZ0 is an evolutionary intermediate from the Archaea PurA to PurZ.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Education Department of Guangdong Province, among other projects. Link to the original article: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-023-01410-1
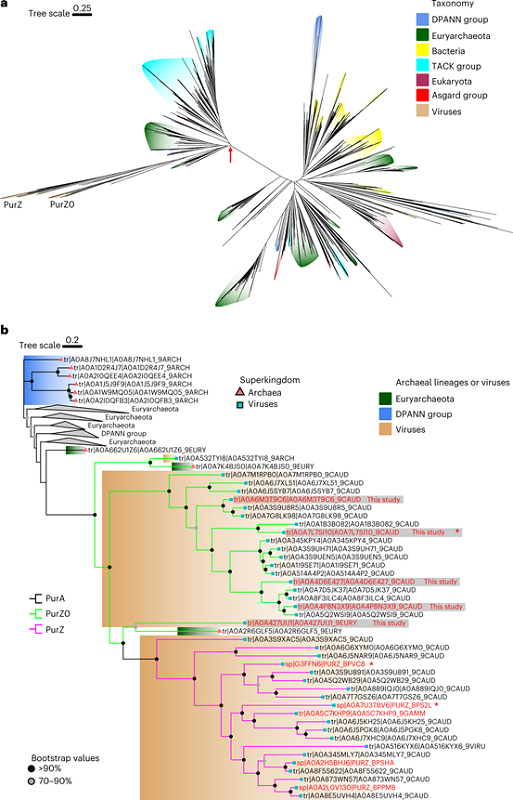
Figure 1 The phylogenetic relationships among PurZA, PurZ and PurZ0


