The latest research from the Pan Research Group at the Institute for Advanced Study of Shenzhen University has been published in the esteemed environmental science journal "Environment International" (SCI Q1, IF: 13.3). The study, titled "Metal leaching from plastics in the marine environment: An ignored role of biofilm," sheds light on the mechanism of metal leaching from plastics in seawater. Dr. Guogan Peng is the lead author of the paper, with Shenzhen University being the primary affiliating institution.
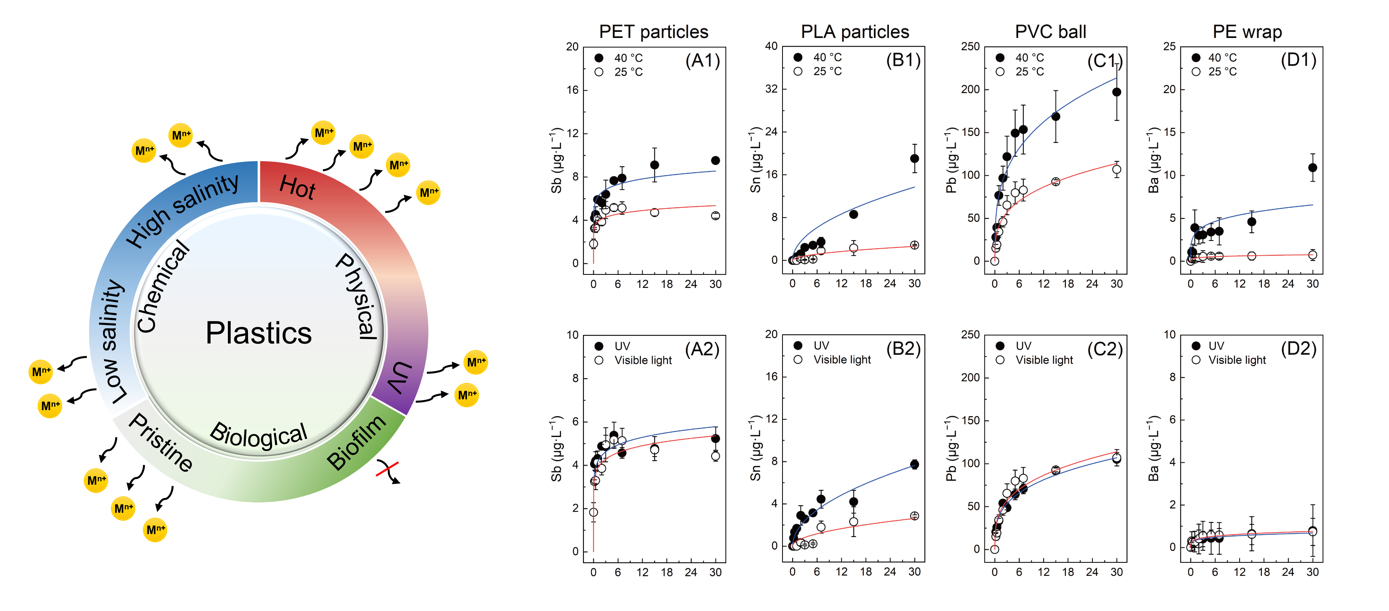
In the production of plastic products, metal additives are commonly incorporated to enhance properties such as durability, flame resistance, and anti-aging capabilities. These additives often lack chemical bonds with the polymer, making them susceptible to leaching upon exposure to the environment. The research team conducted extensive analyses on the metal concentrations of 47 common types of plastics and their raw materials. They evaluated the impacts of environmental factors (temperature, UV radiation, and salinity) as well as the physicochemical characteristics of plastics (surface roughness, specific surface area, hydrophobicity, and crystallinity) on metal leaching. The findings revealed that elevated temperatures significantly increase metal leaching, while the effects of UV radiation and salinity depend on the polymer type. Correlation analyses highlighted crystallinity as a pivotal factor governing the rate of metal leaching.
Furthermore, the research team exposed plastics to coastal seawater environments to study the influence of biofilm on metal leaching. The leaching of metal additives from plastics was prominent within the initial three weeks, followed by a deceleration attributed to the inhibitory role of biofilm. The study offers insights into the mechanism of metal leaching from physical, chemical, and biological perspectives, contributing to the understanding of environmental risks associated with plastic pollution.
This research has received support from various sources, including the Guangdong Provincial Fund, Shenzhen Municipal Science and Technology Innovation Commission, and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
Original Article Link:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2023.107988