Recently, Prof Shern-Long Lee of IAS at Shenzhen University has published in J. Mater. Chem. C (IF: 7.1) a research article related to an electroanalytical method for sensing arsenic in drinking water. The paper title is “Synthesis and sensing efficiency of bioinspired CN wrapped ZnFe2O4 microspheres-ionic liquid composite towards ultra-high sensitivity arsenic(III) monitoring of ground drinking water”
The prerequisite for human health is to have clean drinking water. In water, arsenic(As) among all other contaminants presents a challenge in analytical chemistry field due to the high toxicity of As(III) that can cause serious influence for human health even at very low concentration levels. In particular, the electrochemical method among others represents a powerful means for As(III) sensing, for which the advantages include fast response time, low detection limit, and high sensitivity. Herein, we report a novel strategy that is to synthesize and utilize ZnFe2O4 microspheres for the sensing purpose, achieving exceptional performance and importantly without the use of expensive noble metals. The good performance can be ascribed to the rich of oxygen vacancies for ZnFe2O4. Finally, to demonstrate the power of our system, we have also tested the As(III)-contaminated ground drinking water in Pakistan.
The first author of this paper is Dr. Awais Saleemi in Prof. Shern-Long Lee’s group (corresponding author). The publication was supported by NSFC (21972095).
Website of the publication link:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2020/TC/D0TC01913E#!divAbstract
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC01913E
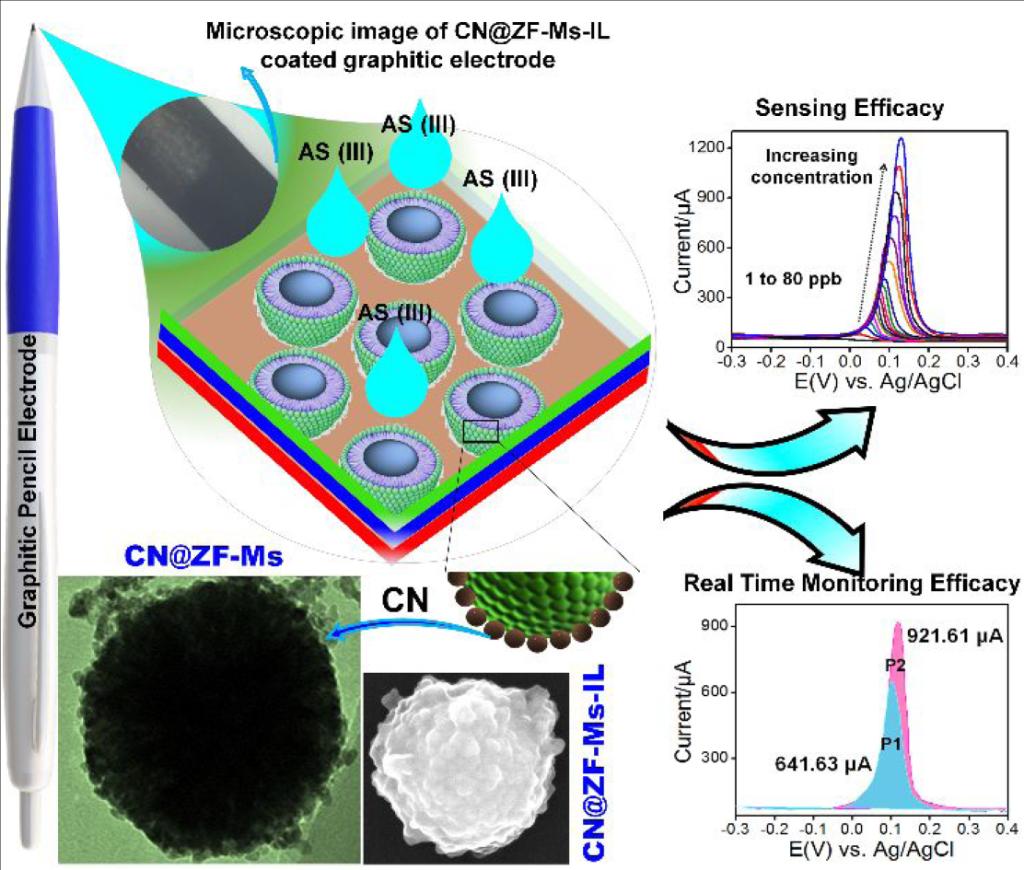
Figure: The synthesis of ZnFe2O4 microspheres for sensing As(III) via square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV) in acetate buffer (pH 6.0).


