On March 12, 2025, Liu'group published a research paper entitled "Retrieval of water cloud microphysical properties with polarized LiDAR based on optimization method: a polarimetric Monte Carlo simulation" in the journal Optics Express. Dr. Wiqas Ahmad, a Postdoctoral Fellow from Institute for Advanced Study, Shenzhen University, is the first author. Huizeng Liu is the corresponding author. Institute for Advanced Study of Shenzhen University is the primary affiliation. Co-authors of the paper include Academician Li Qingquan and Prof. Zhu Ping from Shenzhen University.
Global warming has risen rapidly over the past few decades, posing severe human life threats. It is one of the biggest challenges for the scientific community of the 21st century to overcome. Clouds play a crucial role in the Earth’s radiation budget by increasing the reflection of incoming short-wave solar radiation and reducing outgoing long-wave radiation. They reflectthe incoming solar shortwave radiation back to space, causing cooling of the Earth surface. On the other side, clouds absorb some of the longwave radiation that the Earth’s atmosphere emits and reradiate it back to the Earth surface, producing a warming effect. Furthermore, decreasing cloud droplet size causes an increase in the shortwave albedo, which results in atmospheric cooling that can be used to offset the global warming. In addition, the distribution of these droplets also affects the emissive properties of the water cloud. The water content in the cloud, if distributed in tiny and numerous droplets, extinguishes more radiation than if it is distributed in relatively large and few. Thus, the cloud microphysical properties are closely linked with its radiative properties.
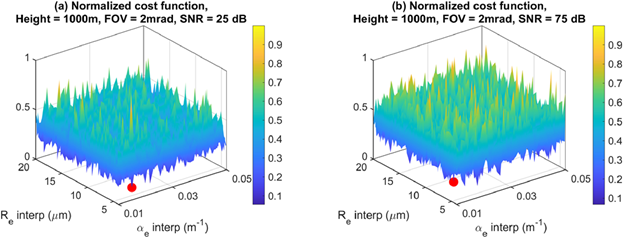
To characterize the microphysical properties of water clouds, such as liquid water content (LWC) and cloud droplet number concentrationwith polarized atmospheric LiDAR, two key parameters are of primary important: the cloud droplet effective radius and the cloud extinction coefficient. However, solving the LiDAR equation to derive these two parameters is ill-posed problem. In this study, we introduce a method based on an optimization for retrieving the water cloud basic retrieval parameters, cloud droplet effective radiusand cloud extinction coefficientthat solve the LiDAR equation using a single field-of-view (FOV) polarized LiDAR simulation. The simulation results demonstrated that the global minimum of the cost function, applied to the look-up table, corresponds to the inversion result. The optimization method employed a grid search algorithm to find the optimal values of the cloud droplet effective radius and extinction coefficient that minimize the cost function.
The optimization method creates a matrix of all possible combinations and evaluating each using the mean squared error. The combination with the lowest normalized cost function value was selected as the optimal parameters set. The results indicated that, despite the complex topology of the cost function, the approach successfully converged to the global minimum, providing the optimal values of cloud droplet effective radius and cloud extinction coefficient providing solution to the inverse problem of the LiDAR equation without complicated inversion techniques. These optimized values can be used to determine the microphysical properties of water clouds close to the cloud bottom, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed retrieval method and its potential for enhancing our understanding of cloud properties through polarized LiDAR observations.
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42371337), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2023A1515011946 and 2024A1515011388) the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (Grant No. JCYJ20230808105709020 and JCYJ20240813142621029), and the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research (Grant No. 2023B0303000017).
Research findings have been published in the journal of Optics Express:
·Wiqas Ahmad, Huizeng Liu, Ping Zhu, and Qingquan Li, Retrieval of water cloud microphysical properties with polarized LiDAR based on optimization method: A polarimetric Monte Carlo simulation. Optics Express, 33(6): pp. 12953-12969 (2025)https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.549620