Xiuting Li’s group at the Institute for Advanced Study successfully developed a highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for the acidic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) by incorporating ruthenium (Ru) and iridium (Ir) metals into spinel-structured Co₃O₄. On September 1, 2025, the relevant research paper, titled "Dual Doping of Ruthenium and Iridium in Octahedral Sites of Spinel Co₃O₄ Nanoflowers for Enhanced PEM Water Electrolysis", was published in Small.
The exploration of highly active and durable OER electrocatalysts remains a significant challenge in acidic proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE). Herein, a ruthenium-iridium co-doped spinel cobalt oxide (RuIr-Co₃O₄) nanoflower electrocatalyst with low noble metal loading (2.7 wt% Ru and 0.25 wt% Ir) was designed for acidic water electrolysis. This catalyst exhibits outstanding performance in acidic water electrolysis: it only requires an overpotential of 220 mV to drive a current density of 10 mA cm⁻², and maintains excellent stability over a 600-hour operation period. When integrated into a proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer, a cell voltage of merely 1.67 V is sufficient to achieve a current density of 500 mA cm⁻².
The study reveals that both Ru and Ir can substitute the Cooct sites in Co₃O₄, thereby strengthening the Co-O bonds and enhancing the electrocatalytic activity. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate that the Ir-O-Co dual-active metal sites are in an optimal configuration, facilitating the direct coupling of oxygen radicals. The acidic OER process on the RuIr-Co₃O₄ catalyst follows the oxide path mechanism (OPM). By regulating the electronic structure through dual-metal atomic doping, this work provides important insights for the development of low-cost, high-efficiency catalysts for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis applications.
Paper link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smll.202509147
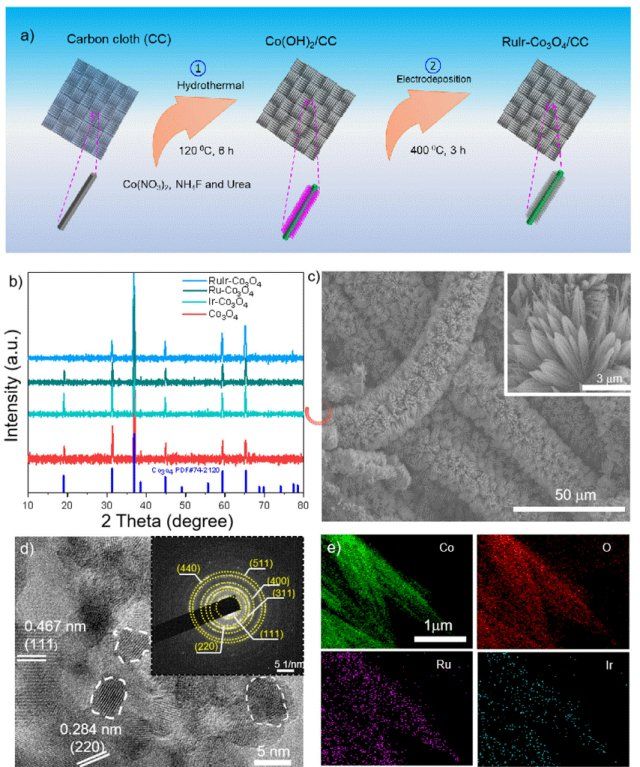
Figure 1. Synthesis and structural characterization of RuIr-Co₃O₄ catalyst. a) Schematic illustration of the synthetic process. b) XRD of RuIr-Co₃O₄, Ru-Co₃O₄, Ir-Co₃O₄ and pristine Co₃O₄. c) SEM images of RuIr-Co₃O₄. d) HRTEM image of RuIr-Co₃O₄, with the inset displaying the corresponding SAED pattern. e) EDS mapping of RuIr-Co₃O₄.


